Featured Products
Cumulative exposure of 5.4 days results into large image of 200,000 light years away group of galaxies.
NASA’s 160-megapixel ultraviolet photography mosaic of a galaxy cluster has been made available by astronomers thanks to the Swift Telescope. This Ultra-Violet / Optical Telescope (UVOT) uses a Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) fitted with 11 position filter wheels. It helped creating high resolution images of the Large Magellanic Clouds (LMC) and Small Magellanic Clouds (SMC) – our two nearest galaxies.
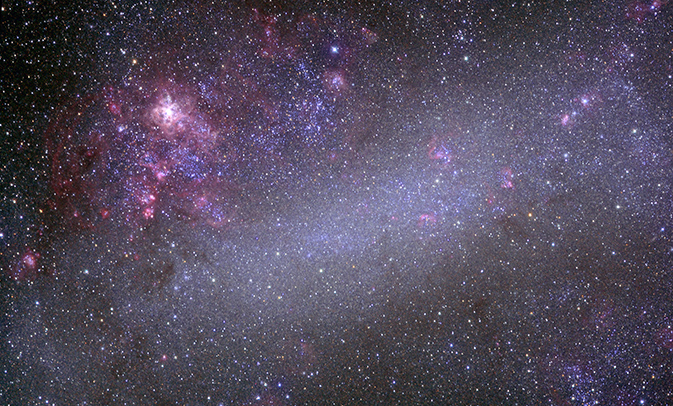

The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) as seen in UV light through Swift telescope. Credits to Axel Mellinger, Central Michigan University
160-megapixel ultraviolet photography mosaic of our neighboring galaxies
Thousands of images were assembled by astronomers at NASA and Pennsylvania State University to reveal each galaxy grouping in the closest cloud to our Milky Way.
Deprived of the real form and color pattern of the Universe by the Earth’s atmosphere and by the closest stars, a standard device couldn’t have captured such details.
Ultraviolet photography, on the other hand, helps suppressing this problem. Furthermore, more than 2,000 images were needed to complete the puzzle.
Tech facts on Swift’s UVOT inner-workings as provided by NASA
Narrow-fields were selected at first by astronomers. And by narrow, they mean quite a huge stretch of space, containing about 250,000 ultraviolet sources. Cumulated exposure time goes over five days with an angular resolution of 2.5 arc seconds. Sharpness is thus as high as capturing a dime from one mile away.
The ultraviolet photography is merged with the optical background to check positions. This is possible thanks to the Swift’s UVOT ability to produce high-resolution wide-field multicolor surveys.
The telescope has a 30 cm reflecting mirror, and several light filters, such as the white light filter. It also makes use of a field magnifier, and UBV wavelengths limiters.
Astronomers can check whether the galaxies are moving away from us or they are getting closer. Redshift burst measurements tell this based on the light spectrum, which can turn towards red or blue.
Astrophotography at the highest levels
You can download high quality photos of the Swift’s LMC mosaic from NASA, at a 16000 x 10000 resolution, in TIFF or JPG format.The Goddard Space Flight Center is behind the entire effort of assembling sections of the main body of each galaxy.
Images and video files provide the best imagery of these galaxies. Scientists taking part in this mission explain the process in several quick tour videos. The movie quality goes up to 1080p.
Can we see the Magellanic Clouds with everyday equipment?
It is possible to see our neighboring galaxies from the Southern Hemisphere. The Large and Small Magellanic Clouds are visible as glowing patches on the night sky. If light pollution interferes with the view, neither of these galaxies or others will be visible.
The Swift Missions Operation Center has solved this problem by taking the telescope into space. An international team dedicated itself to providing a complement to the even narrower field of imagery Hubble telescope was capable of.