Featured Products
NASA used a new laser communication technology to beam a black-and-white photo of Mona Lisa into space.
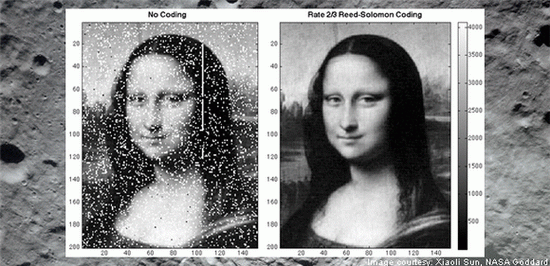
The black and white Mona Lisa image beamed into space by NASA
Mona Lisa is one of the most famous paintings in the world, attracting thousands of visitors at the Louvre Museum in Paris. It was painted by Leonardo Da Vinci between 1503 and 1506 in oil on poplar. It depicts the wife of Francesco del Giocondo, hence the painting’s nickname: La Gioconda. In order to test its laser-based communication system, NASA sent an image of the painting to the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, a spacecraft which orbits the moon and gathers information about the lunar object.
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter on the receiving end of NASA’s Mona Lisa image
Orbiting the moon is no easy task for the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, especially because of the distance from which it receives commands from the space agency. According to NASA, there are more than 240,000 miles between the Goddard Space Flight Center based in Greenbelt, Maryland and the lunar satellite.
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration sent the message to the Lunar Orbiter Laser Altimeter through laser communication. The agency has been tracking the LRO using laser-based technologies since 2006. Laser pulses were sent on a regular basis between the LOLA and space agencies, but this was the first time someone managed to accomplish one-way communication.
How it was made?
Mona Lisa’s image was divided into 152 x 200 pixels, each of them corresponding on a shade of gray. The values of the pixels were beamed one at a time with a bitrate of 300 bit/s. Timing had to be very accurate in order to allow LOLA to understand how to reassemble the photo. Depending when each pulse arrived, the lunar orbiter was able to calculate where to place each pixel.
NASA had to take into consideration Earth’s atmosphere to correct any pixel errors, using the same technique used for correcting CDs and DVDs. All this time the LRO continued with its daily routine, the one which involves mapping the moon.
Laser communication will have enormous implications in future communication technologies
In the distant future, laser communication will allow data transfer at higher bitrates than radio communication, said LOLA lead scientist, David Smith. Soon enough, such technology will be used as a backup for radio communications, added Smith.
The video below provides a more detailed explanation on how NASA was able to beam a Mona Lisa image into space.